The HTTPS specification mandates that HTTPS clients must be capable of verifying the identity of the server.
The basic idea of the URL integrity check is that the server certificate’s identity must match the server host name. This integrity check has an important impact on how you generate X.509 certificates for HTTPS: the certificate identity (usually the certificate subject DN’s common name) must match the host name on which the HTTPS server is deployed.
For example, if a server supports secure TLS connections at the following URL:
https://www.progress.com/secure
The corresponding server certificate would have the following subject DN:
C=IE,ST=Co. Dublin,L=Dublin,O=Progress,
OU=System,CN=www.progress.com
www.progress.com
fusesource.com
subjectAltName=DNS:www.progress.com,DNS:fusesource.com
If the URL integrity check failed, in java code, you probably will get the exception below
java.io.IOException: HTTPS hostname wrong: should be <THE_HOST_USING_HTTPS_CERTIFICATE>;
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.HttpsClient.b(DashoA12275)
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.HttpsClient.afterConnect(DashoA12275)
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.AbstractDelegateHttpsURLConnection.connect(DashoA12275)
at sun.net.www.protocol.http.HttpURLConnection.getOutputStream(HttpURLConnection.java:569)
at sun.net.www.protocol.https.HttpsURLConnectionImpl.getOutputStream(DashoA12275)
at TestSSL.doC8Authentication(TestSSL.java:75)
at TestSSL.main(TestSSL.java:24)
If you cannot change the certificate and have to use it for testing purpose, here is one alternative way to avoid integrity check
HttpsURLConnection con = (HttpsURLConnection)myurl.openConnection();
con.setHostnameVerifier(new HostnameVerifier() {
public boolean verify(String hostname, SSLSession session) {
return true;
}
});
See reference
An alternative way
static {
//for localhost testing only
javax.net.ssl.HttpsURLConnection.setDefaultHostnameVerifier(
new javax.net.ssl.HostnameVerifier(){
public boolean verify(String hostname,
javax.net.ssl.SSLSession sslSession) {
if (hostname.equals("localhost")) {
return true;
}
return false;
//if you don't care host name, return true
}
});
}
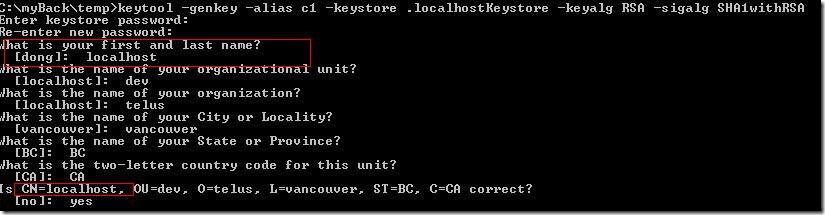
Or you can create a certificate which CN is "localhost". (Let's say the testing server name is localhost.)
No comments:
Post a Comment